Unpacking Unexpected Wheel Strategy Outcomes: Market Dynamics and Key Influencers

Despite the inherent robustness of systematic income strategies like the wheel, even seasoned options traders frequently encounter outcomes that diverge from initial expectations. For instance, the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC) reported over 11.2 billion options contracts traded in 2023, a testament to the market's liquidity yet also a crucible where even well-structured approaches can face unforeseen pressures from macro shifts or idiosyncratic events. Understanding these anomalies is not merely academic; it’s fundamental to optimizing capital efficiency and mitigating tail risk for those selling options.
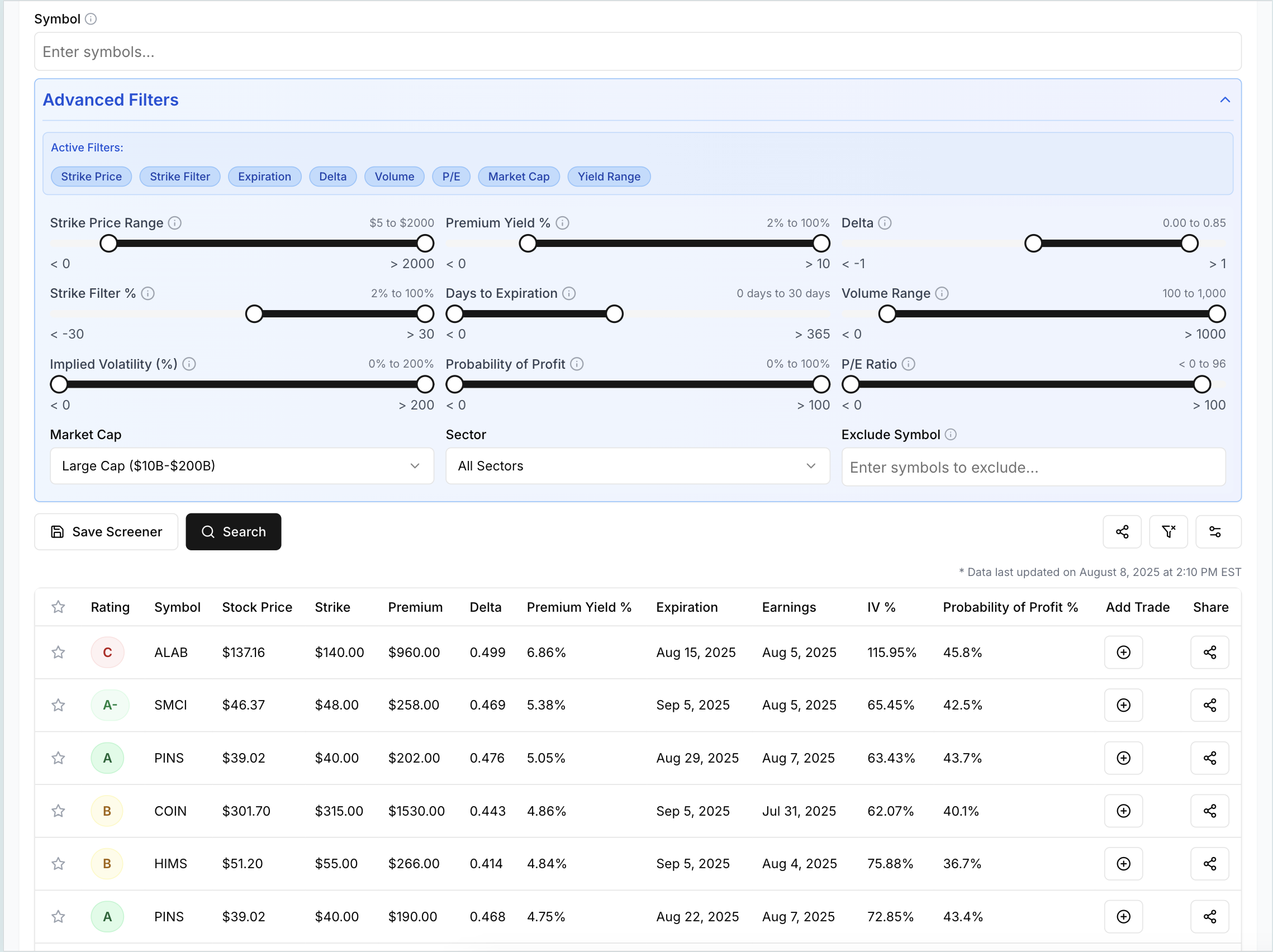
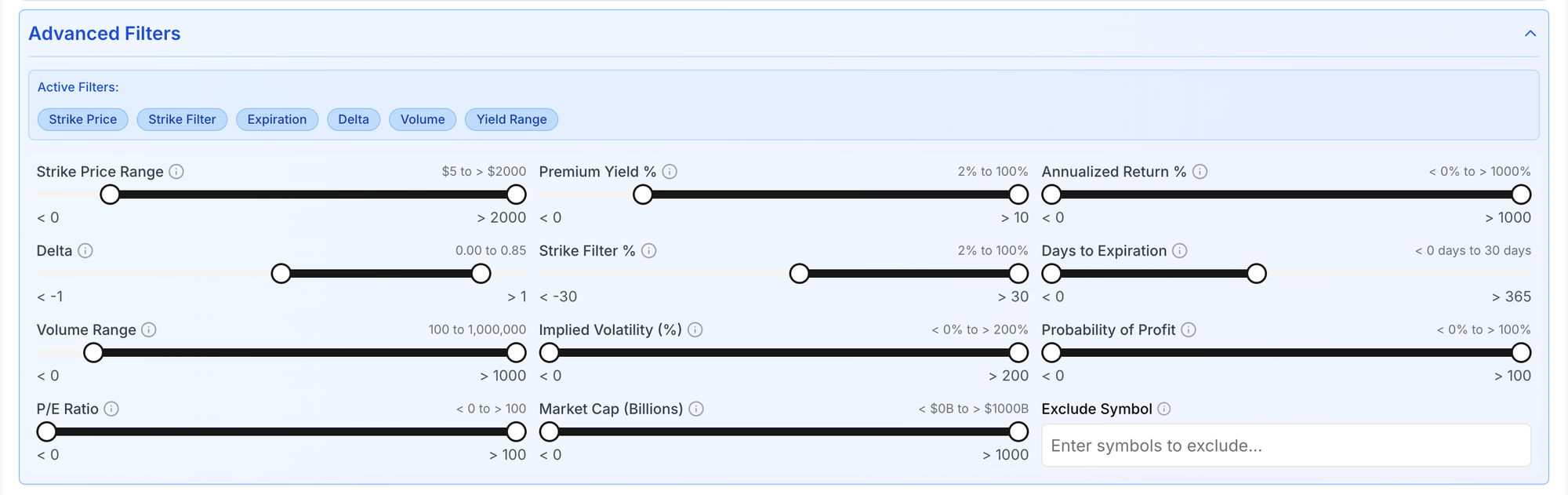
We highly recommend trying our Wheel Options screener here to try out what you learn from this post.
Market Dynamics Driving Unforeseen Wheel Outcomes
The wheel strategy, fundamentally built upon selling cash secured puts and subsequently covered calls, relies on predictable underlying price action within a defined range. However, markets are dynamic, and several forces can rapidly disrupt this equilibrium, leading to unexpected assignment or missed opportunities.
Volatility Surges and Implied Volatility Mismatches
Sudden spikes in market volatility, often signaled by the VIX, can dramatically alter option premiums. While higher implied volatility might seem beneficial for premium collection from selling options, it simultaneously increases the probability of significant price swings. If implied volatility rises sharply post-entry, your short options may be overpriced relative to the new, higher realized volatility, exposing you to greater risk upon assignment. Conversely, a rapid collapse in implied volatility can unexpectedly deflate premium, turning profitable positions into break-even or even losses if the underlying moves unfavorably.
“Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing.”- Warren Buffett
Sector-Specific Shocks and Macroeconomic Headwinds
Even if the broader market appears stable, sector-specific news or macroeconomic data releases can cause outsized movements in individual stocks. A company like XYZ Corp, operating in a sensitive sector, might be highly susceptible to changes in interest rates, supply chain disruptions, or regulatory shifts, all of which can lead to rapid price depreciation or appreciation, challenging a wheel strategy's parameters. Unexpected inflation reports, employment figures, or central bank policy statements can cascade across sectors, impacting even fundamentally strong companies targeted by wheel options traders.
Liquidity Constraints and Bid-Ask Spreads
In highly volatile or thinly traded assets, liquidity can quickly dry up, leading to wider bid-ask spreads. When managing existing covered calls or cash secured puts, executing a roll or closing a position can become significantly more expensive due to these wider spreads, eating into potential profits or exacerbating losses. This is particularly crucial when trying to avoid assignment or manage an already assigned stock.
Key Influencers on Wheel Strategy Performance
Beyond broad market dynamics, specific influences at the company and psychological levels can steer a wheel trade off course.
Corporate Actions and Unscheduled News
Earnings reports are known catalysts, but unexpected corporate actions like mergers, acquisitions, stock splits, or even management changes can introduce significant volatility. Imagine having a short put on ABC Trading Group, only for the company to announce an unexpected share buyback, causing a sharp rally, making your put expire worthless, but potentially forcing you to miss out on significant upside, or conversely, a class-action lawsuit leading to a massive sell-off, forcing an undesirable assignment.
Option Pricing Model Limitations in Extreme Conditions
Standard option pricing models like Black-Scholes have assumptions that break down in extreme market conditions. For instance, the assumption of continuous trading and constant volatility is rarely met during flash crashes or parabolic rallies. This can lead to mispricing, where the theoretical value of your options diverges significantly from the market price, making risk assessment and trade adjustments more challenging.
Behavioral Biases and Market Sentiment Shifts
Human psychology plays an undeniable role. Herding behavior, fear, and greed can amplify market movements beyond what fundamentals suggest. Traders engaged in the wheel strategy might find their disciplined approach challenged by sudden surges of bullish optimism leading to early call assignment, or panic-driven sell-offs forcing undesirable put assignment. Recognizing these biases, both in the market and within oneself, is critical.
“The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient.”- Warren Buffett
Brokerage and Platform Execution Realities
The execution capabilities of your brokerage platform can also influence outcomes. Slippage, latency, and the stability of your trading interface can affect your ability to enter or exit positions at desired prices, especially during fast-moving markets. For sophisticated traders employing a high volume of wheel options trades, even small execution discrepancies can compound over time.
Advanced Risk Management and Adaptation
Mitigating unexpected wheel strategy outcomes requires a proactive and adaptive approach, going beyond basic position management.
Beyond Delta-Hedging: Volatility and Gamma Management
While delta-neutral strategies are common, understanding and managing vega (sensitivity to implied volatility) and gamma (sensitivity of delta to underlying price changes) is paramount. When selling options, particularly out-of-the-money (OTM) cash secured puts and covered calls, vega exposure can be significant. Monitoring how your portfolio’s vega changes with market sentiment and adjusting position size or strike selection based on expected volatility shifts can prevent premium erosion or excessive assignment risk.
Strategic Stock Selection for Wheel Options
Choosing the right underlying asset is half the battle. Focus on companies with robust financials, predictable earnings, and a history of lower volatility, even if it means sacrificing some premium. Evaluate the company's competitive moats, management quality, and industry trends. For advanced traders, incorporating quantitative screens for financial health and liquidity is non-negotiable. Our wheel strategy screener with advanced filters can assist in identifying high-quality underlying stocks suitable for a more resilient wheel strategy.
Capital Allocation and Position Sizing
Diversification across multiple uncorrelated assets can reduce the impact of an unexpected event in a single stock. Furthermore, conservative position sizing ensures that no single unexpected assignment, whether from a cash secured put or a covered call, jeopardizes your entire trading capital. Maintain sufficient free capital to manage assigned shares or open new positions without undue stress.
“The first rule of compounding is to never interrupt it unnecessarily.”- Charlie Munger
Learning from Unprofitable Cycles
Every unexpected outcome, positive or negative, is a learning opportunity. Maintain a detailed trading journal, documenting not just entry and exit points, but also your rationale, market conditions at the time, and the specific factors contributing to unexpected results. This meta-analysis helps refine your selection criteria for wheel options and your adaptive responses to market shifts.
Case Study: Company A's Earnings Surprise
Consider a scenario where an intermediate trader initiated a wheel strategy on Company A, a stable tech company. The trader sold a cash secured put with a strike of $100, believing the stock would hold above that level. Premium collected was $2.00. Suddenly, Company A announced a significant earnings miss, causing the stock to gap down from $105 to $90 overnight.
| Action | Expected Outcome | Actual Outcome | Impact on Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sell $100 Cash Secured Put | Stock stays > $100, put expires OTM. | Stock drops to $90, put assigned at $100. | Unexpected assignment, holding stock at a loss (cost basis $98). |
| Write Covered Calls (post-assignment) | Write calls above $100 to reduce cost basis. | Stock range-bound between $88-$92 for weeks. Calls written at $95 yield minimal premium. | Difficulty recovering losses, extended capital tie-up. |
| Strategy Adaptation | Roll puts/calls or take assignment. | Considered selling call credit spreads or put debit spreads to hedge assigned stock, or cutting losses. | Forced into more complex adjustments or realizing a loss outside the original wheel parameters. |
This example highlights how a single, unforeseen event can disrupt the entire wheel cycle, forcing difficult decisions regarding loss management or adapting to a new, less favorable cost basis for the assigned stock. It underscores the importance of thorough due diligence and an understanding of potential catalysts when selecting an underlying for wheel options.
Summarizing Key Takeaways
- Unexpected outcomes in the wheel strategy stem from a complex interplay of market dynamics, specific company events, and behavioral factors.
- Advanced traders must look beyond basic premium collection to understand how volatility shifts, liquidity, and macroeconomic headwinds impact their short options positions.
- Strategic underlying selection, rigorous risk management (including vega/gamma awareness), and conservative capital allocation are crucial for building resilience.
- Leverage tools like a wheel strategy screener to identify suitable, higher-quality underlying assets for selling options. You can even save your setup and be alerted automatically when contracts hit your desired criteria.
- Every unexpected outcome serves as an invaluable lesson for refining your approach to the wheel options strategy.
Disclaimer: *This blog post is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Trading options involves risk of loss. Conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.*
Follow us on:
Threads | X (Twitter) | Reddit | Instagram
Comments ()