Calculating Option Premiums: A Deep Dive into the Black-Scholes Model

Introduction
Options trading offers a flexible approach to managing risk and enhancing returns. Understanding how option premiums are determined is crucial for informed decision-making. This article delves into the Black-Scholes model, a widely used method for calculating theoretical option prices.
Understanding the Black-Scholes Model
The Black-Scholes model uses several key inputs to calculate an option's theoretical price. These inputs include:
- Underlying Asset Price (S): The current market price of the asset the option is based on (e.g., stock price).
- Strike Price (K): The predetermined price at which the option holder can buy (call option) or sell (put option) the underlying asset.
- Time to Expiration (T): The remaining time until the option contract expires, expressed as a fraction of a year.
- Risk-Free Interest Rate (r): The return an investor can expect from a risk-free investment, typically a government bond.
- Volatility (σ): A measure of the underlying asset's price fluctuations. A higher volatility implies greater price swings and generally leads to higher option premiums.
The model utilizes these factors in a complex formula to calculate the theoretical price of a European-style option (an option that can only be exercised at expiration).
Example Calculation
Let's consider a call option on the fictional stock "ABC Corp." with the following parameters:
- S = $100
- K = $105
- T = 0.25 (3 months/12 months)
- r = 0.02 (2%)
- σ = 0.3 (30%)
Plugging these values into a Black-Scholes calculator (available online), you can find the theoretical call option premium. Let’s assume the calculator gives us a theoretical price of $2.50.


Pros and Cons of the Black-Scholes Model
Pros
- Provides a theoretical framework for valuing options
- Helps understand relationships between option price and various input factors
- Widely used and accepted in the financial industry
Cons
- Assumes constant volatility, which is not realistic in real-world markets.
- Doesn't account for dividends or early exercise (relevant for American-style options).
- Can be complex to implement manually.
Risk and Benefits of Using the Model
While the Black-Scholes model provides valuable insights, it is essential to remember that it provides a theoretical price. Actual market prices may deviate due to supply and demand dynamics, market sentiment, and other factors. Using the model in isolation carries the risk of mispricing options. The benefit lies in understanding the relationship between the factors influencing option prices and obtaining a benchmark for evaluating market prices. Always consider additional factors, such as market conditions and your own risk tolerance, before making trading decisions.
Interpreting Results in Different Scenarios
Let's explore how changes in inputs affect the option premium using the ABC Corp. example:
- Increased Volatility: If volatility increases to 40%, the call option premium would likely increase, reflecting the higher potential for price swings.
- Longer Time to Expiration: If the time to expiration extends to 6 months (T=0.5), the premium would also likely increase, as there’s more time for the underlying asset price to move favorably.
- Higher Interest Rates: A rise in interest rates generally increases call option premiums and decreases put option premiums.
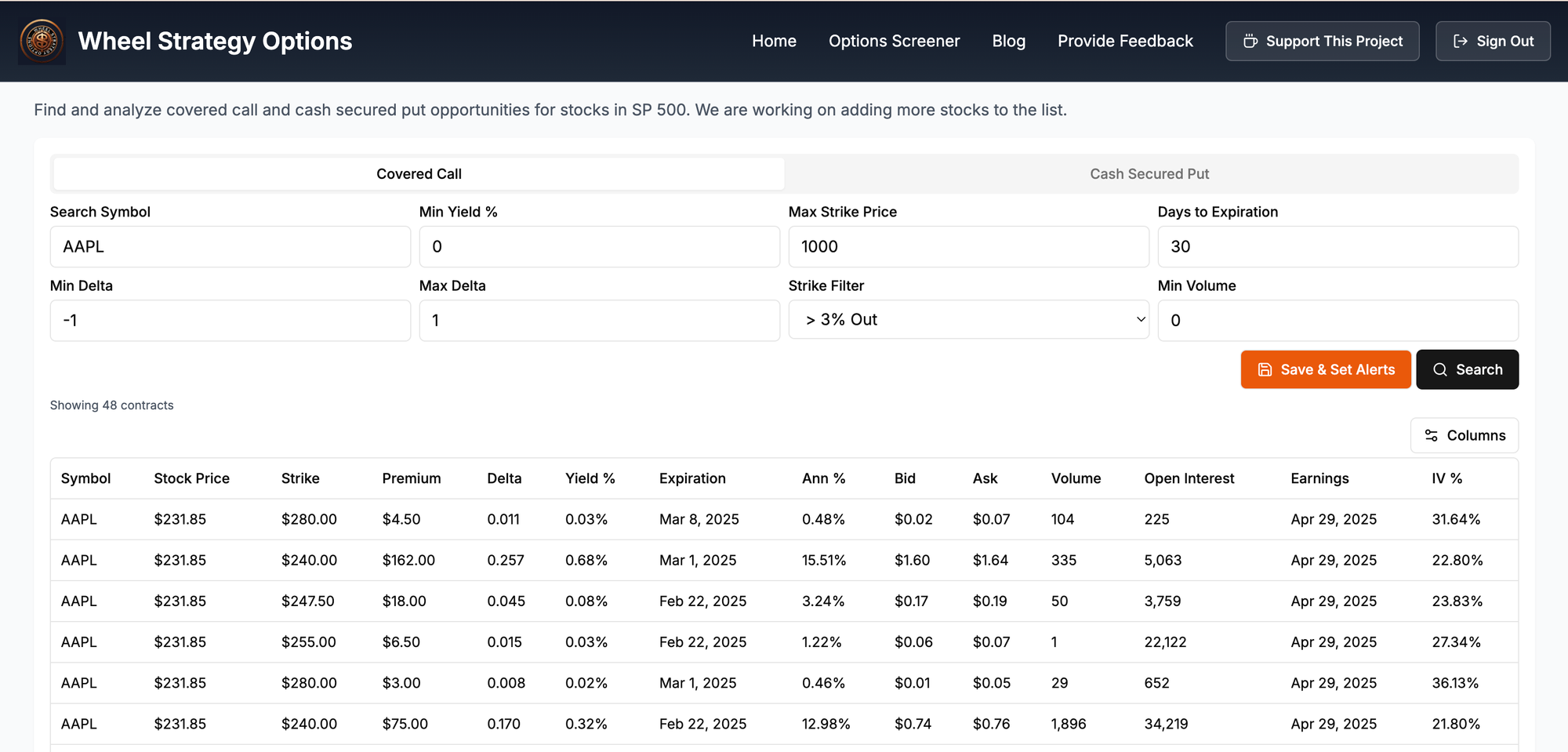
If you are looking to dominate the options game, this options screener delivers high-yield options trades maximizing premium income with intelligent filters. Select your strategy, set alerts and be notified of trades that match your strategy.
Disclaimer:
This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Investments are subject to risk, and you should carefully analyze any investment before making decisions. Consult with a qualified financial advisor for personalized guidance.




Comments ()